Overview for normal glucose digestion and diabetes mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus – Imagine your self tracking the fate of carbohydrates you eat starting with your digestive system, blood, then each cell in your body. Don’t you want to know how does your body digest carbohydrates?

Today, we are going to discuss the normal digestion of carbohydrates, and the abnormal digestion that results in Diabetes Type 1 and Diabetes Type 2.
When you eat a carbohydrate source like bread, potato, etc…Your body can see it either as a simple structure or a Complex; by the means of that, the body does not see bread or potato, instead; the body sees it as compounds. Thus, the body either find these compounds Simple and easy to use or Complex and needs to get simpler. In both scenarios, your body translates it into a source that it can be used for building up itself or as an Energy source. For energy, the cells mostly use the Simple form of carbohydrates which is glucose.
Then the glucose is absorbed through the mouth, stomach, and gut to your bloodstream, to be distributed and taken up by every cell in the body. Let’s discuss how particularly Glucose is absorbed in the mouth, stomach, and gut😉.
To breakdown complex structures there are tools and helpers that our body uses called “Enzymes”. In the mouth, there is an enzyme called “Salivary Amylase”, which provides our body with the needed glucose from complex compounds.
If that is the case through the mouth. So,
Why do you need the stomach and the gut?
The mouth can only perform a small part of the job. Imagine yourself eating, the food does not remain in your mouth for more than a couple of seconds! How could it be fully digested? Thus, we need our stomach, where the involuntary digestion technique starts to take the lead.
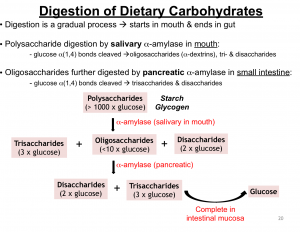
Your stomach turns to be acidic through“hydrochloric acid” when food reaches the stomach. This results in the inactivation of salivary amylase and breakdown of complex structures as well. The stomach and gut perform the major breakdown and the whole glucose intake is now in the gut.
Is that the end of glucose fate?
Actually no, do not forget that all this is for the sake of energy for cells.
Our body is in natural biological and chemical balance with itself and its surroundings, for every minute or even every second and millisecond through its inner regulation, Which estimates through feedbacks of molecules, electrolytes, Enzymes, Hormones, etc…
This is the circle of life. For glucose, there are two main important hormones for its regulation between blood levels and cell’s internal levels; insulin and glucagon.
How does glucagon work?
- During Fasting
Glucose levels are low in the blood and also in the cells, so from where to get glucose?
Our body according to its normal physiology is prepared, as it is storing glucose in the form of glycogen in the liver, muscles and in the form of fats in adipose tissue. So, the low levels of insulin and indirectly glucose stimulates the secretion of glucagon from the pancreas. glucagon works on the liver and muscles mainly to breakdown glycogen to glucose, then glucose is released into the blood.
- During starvation
Your blood levels of glucose are low, Your liver and muscle stores are mostly diminished, so the body starts to breakdown your muscles and fats. So, your body wastes muscle and fats.in which increases the level of blood acidity, which puts your brain in a dangerous situation.
How does insulin work?
- During Feed state:
In this case, your blood contains a lot of glucose, The high blood glucose level sends a signal to the pancreas to produce Insulin. There are cells which depend on Insulin to uptake glucose from the blood:
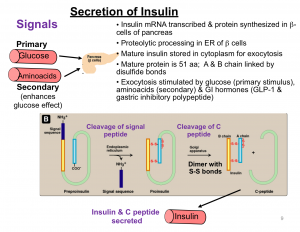
- 70% of skeletal muscles
- 10% of Adipose tissue
- There are also cells which do not depend on insulin for glucose uptake
- Brain cells
- Liver
- Blood vessels, But blood vessels function which controls blood pressure depends on Insulin
- Kidney
- Pancreas
- reproductive system gland
In a study published in the Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology March 2019 that glucagon higher than normal levels can increase insulin resistance as it opposes Insulin actions.
Another study of the modern approach of clinical trials in the Chinese Journal of physics in October 2018; they are experimenting with the principle of using artificial pancreas, And they found out that glucagon plays an important role in balancing glucose level besides sensitizing the pancreas to produce Insulin.
So, what happens when the body cannot use Insulin right?
What is diabetes mellitus?
Glucose accumulates and the main energy consumed source is diabetes mellitus is a chronic(life long) condition of high blood glucose level in the blood. To get deeper into body functionality the problem is hormonally caused by Insulin which is secreted from the pancreas. Also, it depends on your body’s response to Insulin through what is called “Insulin Receptors”.This is located on the targeted cells, According to the Insulin’s level secretion and your receptors response, there are different types of diabetes.
N.B: Brain is the first and the most affected by Glucose insufficiency. It is affected if Glucose levels are low or there is an increased acidity.
Types of diabetes are many, but let’s start with
Diabetes mellitus type1
Diabetes Type 1 has two other names which are “Juvenile diabetes” and “Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus”.Juvenile diabetes indicates that type1 occurs commonly during childhood and in young adults as a genetically and immunity-mediated disease, doctors, researchers, and pathologists through research and health care, found the cause for the genetic mutation or change to be unclear. However, in rare cases, it may happen later in life and in this case called late-stage diabetes mellitus.
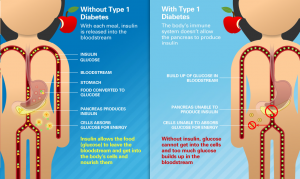
Diabetes Type 1 is an autoimmune disorder, where there are a susceptible person and an environmental trigger; According to study published in medicine Journal on January 2019 performed on twins that were from one zygote(The first cell producing human beings after a combination of ovum and sperm, in case of twins coming from one zygote division, they have identical genes), one of them could arise Diabetes Type 1 while the other not, this observation was one of the strongest evidence that provided that there are environmental contribution for type 1. According to the population, it occurs in (5-10%) of the total number of diabetes cases.
The insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) relates to the patient’s method of treatment, In type 1 patient’s pancreas is not synthesizing Insulin. As a result, they are on Insulin supply through daily injections.
There are four main stages for developing Diabetes Type 1, let’s go through them all so that you can have a better image.
What are the 4 stages?
Stage 1.
No symptoms (pre-clinical) stage, Here the patient’s immune system produces antibodies directed towards beta islets (Type of pancreatic cells which is responsible for Insulin secretion). This stage is known through the presence of markers(A medical indicators that can be found in the blood.It tells you if the disorder is happening or already present). Not all beta cells are destroyed, there are cells still functioning.
By the way, the absence of markers does not indicate the absence of the disease. So we can say markers are indicators and not confirmatory medicine journal, January 2019.
Stage 2.
Symptoms occur with high blood levels of glucose, From, 80%-90% of cells are destroyed, so there is almost no Insulin.
Stage 3.
It is called the transient stage or called “ honeymoon stage”, The remaining 20% of cells exert more than a normal effort in trying to compensate for the great loss of cells and Insulin.
Stage 4.
Complete destruction of cells, the end-stage.

Thus, this is the Insulin requirement throughout the disease progression.
Trying to decrease factors that may trigger the body’s Immune system. Here are some which may cause antibodies to attack our beta cells:
- virus
- cow milk
- vitamin D deficiency
- Gluten
- Pancreatic inflammation
- Family history is a risk, 1 to 50-100 person if the mother has Diabetes Type1, 1 to 10 if the mother and one of the relatives have it
Symptoms of diabetes type 1
To memorize three of them; Here are the 3Ps:
- Polyuria(increased amount of urine excretion).
- Polydipsia(increased thirst).
- Polyphagia(increased appetite).
Here comes the explanation part of these symptoms 😉.
Your kidney has the ability to return a certain amount of glucose filtered by it to the blood. When the blood glucose is high, It exceeds the kidney’s limit. Thus, the kidney starts to eliminate the excess in urine (Giving the characteristic odor of diabetic patients’ urine). There is something called fluid osmolarity. Here, we mean by fluid (blood, urine …etc). And for the osmolarity, It is formed by electrolytes (sodium, potassium,…etc, molecules as Glucose). When it is higher than normal, your body starts to normalize it through excreting the excess, or finding a compensatory to lose instead of the excess and loss of water. The high Osmolarity drives excess glucose out in urine and water. That’s why the urine volume increases and you feel thirsty.
That is for increased urine and thirst symptoms, but what about hunger?
When your Insulin that drives Glucose inside cells is low, or there is no response from the cells to it. The cells feel starved for Glucose. Accordingly, the body reacts like as if it is in a fasting state, and it sends signals to your brain saying“I’m hungry”. As a result, your brain sends a signal back to your stomach to secrete digestive Enzymes, which gives you the feel of hunger.
One of the most dangerous symptoms is Ketoacidosis. It happens when there is a complete absence of Insulin. Usually, this occurs in the last-stage or in DiabetesType 1 patient; who do not take their Insulin (i.e; The need for insulin for survival). In Ketoacidosis, the proteins and fatty acids are used excessively for Energy instead of Glucose, producing high levels of acids in the blood, which is extremely dangerous. Especially, for the Brain, as it leads to coma and death.
Symptoms of Ketoacidosis:
- Rapid weight loss, patients usually are thin(lean)
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- sores, do not easily heal
- Numbness in feet
Diagnosis for Diabetes type 1
According to a study published in April 2009 to relate something unexpected to diabetes Type 1 in young adults and Sleeping. they found sleeping depth and insomnia, short duration of sleep present for poor diabetes control. Also, there is a correlation in Diabetes Type 2.
Fasting blood glucose, to fast from 8-12 hours only drink water (be aware to drink normally and not too much, to avoid diluted blood that gives false results). You diagnosed as diabetic if your readings are greater than or equal to 126 milligram/decilitre(7 millimoles/liter).
Random blood glucose level, which from the name measured at any time without fasting.
According to the American Diabetes Association(ADA), you are diabetic if your readings are greater than or equal to 160 mg/dl(11.1 mmol/liter).
Glycated hemoglobin test which used for monitoring. Usually, your hemoglobin has different types, one of them called hemoglobin A1C or glycated hemoglobin(Hb A1C); A type which is the product of hemoglobin combination with glucose, its normally present to a certain limit. this type used to monitor diabetic patients whether they are under control or not and may help in diagnosis(not used alone for diagnosis). And the reading of Hb A1C is greater than 6.5%.
This is all for the causes, symptoms, and diagnoses of diabetes type 1. Now, we will discuss the same parameters for diabetes type 2. C-peptide a breakdown product of Insulin, can be used as a differential key between Diabetes Type 1 and Diabetes Type 2, In the case of Diabetes Type 1, it is very low or mostly absent.
Diabetes mellitus type 2
A slow-developing type which has a wide prevalence (90% of diabetic patients) due to the fact that it occurs in middle-aged adults and related in usually with obesity, commonly people beyond 40 years old. The pancreas doesn’t produce or synthesize enough insulin for the body requirement, or there is the resistance of the cells to insulin. In conclusion, Diabetes type 2 may require insulin or other approaches. Formerly, they call it ‘non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus’.Because most patients either take medications and just adjust their lifestyle. However, late-stage patients, unfortunately, need insulin.
Here is borderline diabetes:
It does not consider diabetes but it is an alarm for developing diabetes type 2. The good news is, It’s a reversible state.
If you are pre-diabetic:
Fasting blood glucose: (100-125) mg/dl.
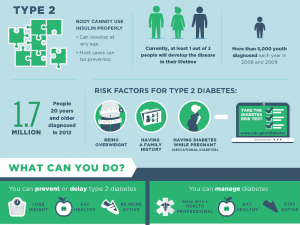
Our body not just directly jump to diabetes mellitus; what happens actually graduated:
- First, there is resistance to Insulin.
- As a response, the body increases the secretion of Insulin as it gets false feedback from starving cells and high glucose in the blood.
- More and more exhaustion of beta cells leading them to be unable to function anymore.
- Liver and muscles breakdown their glycogen storage, increasing blood glucose more.
- Fat tissue break to fatty acids, increasing the resistance furthermore.
Causes of diabetes mellitus type 2
- Obesity
- Our liver and kidney store glucose in the form of glycogen(poly-glucose)
- Muscles store a major amount of glucose
- Fat tissue stores minor amount of glucose
During Obesity your LDL level is high (bad cholesterol; If it is high you are at high risk of atherosclerosis; narrowing of arteries due to fat accumulation on its wall). Studies found that high levels of LDL associated with increased insulin resistance, as well as fatty acids(products of fat cells breakdown), both impair liver, muscle normal glucose pathway. Increasing the breakdown of glycogen despite high blood levels of glucose and Impaired insulin resistance.
- Family history of Diabetes Type 2 and Obesity.
- Anti-Insulin hormones(Hormones which oppose the action of Insulin) as cortisone, growth hormone, increased secretion of thyroid hormone. These Hormones exhaust the Pancreas and damage cells.
- Drugs, as glucocorticoids(used in the treatment of inflammation), psychiatric drugs, drugs used to decrease LDL(It has a possibility of causing diabetes but a benefit of protecting heart and brain dangerous consequences), certain types of diuretics.
- Disturbance of circadian rhythm Increases Insulin resistance.
Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes:
- Fasting and random glucose.
- Hb A1C.
- Fast strips by just one drop of your blood. It is famous now and one of the widely useful methods for anyone. So, doctors use it as a fast and easy test.
- C-peptide is high or low in the case of Diabetes Type 2.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
:
- The same as type 1 (3P’s, Fatigue, blurred vision, sores, numbness), but not commonly weight loss.
- Patients usually are Obese or overweight.
- No Diabetic Ketoacidosis despite that, the patient is also susceptible to common under no control of blood sugar levels.“Think about it: heart disease and diabetes, which accounts for more deaths in the USA and worldwide, can be completely preventable by making comprehensive lifestyle changes. Without drug or surgery.” Said Dr /Dean Ornish, Cardiologist and health advocate. And this approach we will discuss in one of our coming articles 😉.
Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death all over the world. So, It is not just a sole disease or danger, It is actually a start that leads to a chain of complications.
When a study performed past March 2019 for applied nursing researches on young diabetic women; It concluded three important themes:
- Frustration and stigma lead to the inability of the patient to follow up.
- Low income froze them.
- Social support improved the detachment of care.
And now we have covered the causes, symptoms, and diagnoses of Diabetes Type 2. This is not the end of our Diabetic topic, there is still much to discuss. Wait for the next article that will be about prediabetics. Is it a oneway approach and diabetic is your destiny, or finally the researchers have found a glimmer of hope for prediabetics to pass this phase peacefully and get back to normal.



Very informative blog thanks.
I agree raman
Right @raman
Yes I do agree Raman
Thanks for the info, good one 🙂
Yes I do agree good detailed information stated in the blog
Will love to check similar stuff and will definately come back
Thankyou👍
God bless you people a very good work I must say…
I am impressed with the info the writer gathered for us… Diabetes management is very necessary as it starts destroying our health like a termite.
Nice Blog😀
Good info👍
[…] imbalance of our GI bacteria with an increased likelihood of obesity. Probiotic supplementation may decrease the risk of type 2 diabetes and lower cholesterol levels in the […]